Botox® Therapy | DBS Therapy for Parkinson's and Essential Tremor
Botulinum toxin or Botox® has been proven to be extremely effective for treatment of both migraine and tension type headaches. Botox has been used to treat many different neurological conditions including certain types of movements disorders such as torticollis, cervical dystonia, belpharospasm... etc. The benefits of Botox therapy was in many ways discovered "accidentally" by physicians who were providing Botox for cosmetic purposes. Many patients felt their headaches and migraines were significantly relieved following administration of Botox.
How does it work?
Intense clinical and basic science research done with Botox has revealed the likely mechanism by which Botox treats migraines. In short, Botox works by stopping the release of chemicals in the brain that cause muscle contraction, pain, and inflammation within the scalp and face. Numerous animal and human clinical trial involving hundreds of patients show that Botox injections significantly reduce both the intensity and frequency of headaches.
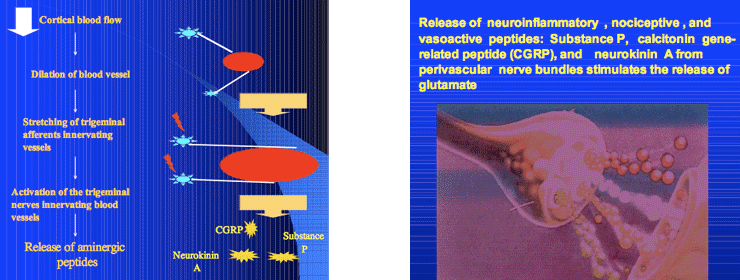
This diagram shows the likely pathophysiology of a migraine attack.
What are the side effects?
Many patients are fearful of Botox because of its name, i.e. "toxin." However, Botox is synthesized, purified, and administered in very small doses that make it very safe and effective. The best part of Botox is that it is not associated with side effects like many medicines. Conventional medical therapy use medications that enter the bloodstream and can adversely affect all parts of the body. Botox is an injection targeted against only the parts of the scalp where the pain is generated and felt. Botox does not have any significant side-effects when administered correctly and at the appropriate dose. Occasionally, some patients experience droopiness of the eyelid with Botox injections given around the eyelids. This effect usually wears off within 6-8 weeks and is very rare.
How long does it take to work?
Botox usually takes 2-3 weeks for maximum benefit. Of course, there is some individual variation--it may take less time or longer as each person's body is slightly different in its response to treatment.
How long does the treatment last?
Most patients feel the benefits last at least 3-4 months. Some can have benefits up to 9 months to a year. Others never need another session as the abnormal cycle of headache and inflammation can sometimes stop with a single session.
How is Botox administered?
Using a very thin needle, Botox is injected into specific muscles of the scalp, face, and neck. Some patients will require fine-tuning of the injection dosage and sites with each session to achieve optimal results. The injection itself causes minimal discomfort at the site of injection.
The figures below shows typical injection sites for Botox:

How much does Botox therapy cost?
Botox is synthesized and purified by Allergan® pharmaceutical to achieve a safe and effective product. The total cost of Botox therapy is individualized with each patient. Health insurance companies often do not cover the cost of Botox therapy for migraines. However, many other neurological conditions that lead to headaches such as cervical dystonia are covered. A careful, detailed examination of the patient is performed to evaluate for neurological conditions that often lead to severe neck pain and headaches which are covered by health insurance. Statistical analysis of the total cost of prescriptions drugs, lost work and productivity, and emergency room visits have shown Botox to be very cost-effective.
Overall, the cost of Botox is individualized for each patient to optimize the benefits and make it affordable. For an estimate, you may call the staff at OCN at: (949) 365-9128.
What other neurological conditions can Botox be used for?
- Excessive muscle spasticity associated with strokes, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury
- Hemifacial spasm (involuntary spasms of face)
- Blepharospasm (involuntary and excessive contraction of eyelid muscles)
- Dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions often seen in the neck, hands, feet,..etc.)
- Head Tremor
- Myofascial neck or back pain (due to excessive muscle spasticity)
- Hyperhidrosis (Excessive sweating of hands, armpits... etc.)


